Extra love for scripting
When we released 8.0 we pushed the most wanted feature: scripting that makes it possible to test multiple pages in a user journey. Since the release we pushed many small additions and I wanted to go through a couple of them.
Better error handling #
The first release didn’t have any fancy error handling, but now you have more alternatives.
You can try/catch failing commands that throw errors. If an error is not caught in your script, it will be caught in sitespeed.io and the error will be logged and reported in the HTML and to your data storage (Graphite/InfluxDb) under the key browsertime.statistics.errors.
If you do catch the error, you should make sure you report it yourself with the error command, so you can see that in the HTML report. This is needed for all errors except navigating/measuring a URL. They will automatically be reported (since they are always important).
Here’s an example of catching a URL that don’t work and still continue to test another one. Remember since a navigation fails, this will be reported automatically and you don’t need to do anything.
module.exports = async function(context, commands) {
await commands.measure.start('https://www.sitespeed.io');
try {
await commands.measure.start('https://nonworking.url/');
} catch (e) {}
return commands.measure.start('https://www.sitespeed.io/documentation/');
};
You can also create your own errors. The error will be reported in the HTML result and sent to Graphite/InfluxDB.
module.exports = async function(context, commands) {
// ...
try {
// Click on a link
await click.byLinkTextAndWait('Checkout');
} catch (e) {
// Oh no, the content team has changed the name of the link!
commands.error('The link named Checkout do not exist on the page');
// Since the error is reported, you can alert on it in Grafana
}
};
Clearing the browser cache #
There’s an experimental command for clearing the cache within scripting. The command works both for Chrome and Firefox on desktop but not on Chrome on Android since we are using a WebExtension. If you need to clear the cache on Android you should use Chrome Devtools Protocol and the clear browser cache command.
There are two functions you can use. Either clear everything cache.clear() or clear everything but keep cookies cache.clearKeepCookies().
Remember that when you start your first script, the cache is already cleared and you are using a new session. There’s no need to start your script by clearing the cache, that happens automatically. The cache is cleared between iterations.
Meta data #
You can add meta data to your script. The extra data will be visible in the HTML result page.
Setting meta data like this:
module.exports = async function(context, commands) {
commands.meta.setTitle('Test Grafana SPA');
commands.meta.setDescription('Test the first page, click the timepicker and then choose <b>Last 30 days</b> and measure that page.');
await commands.measure.start(
'https://dashboard.sitespeed.io/d/000000044/page-timing-metrics?orgId=1','pageTimingMetricsDefault'
);
await commands.click.byClassName('gf-timepicker-nav-btn');
await commands.wait.byTime(1000);
await commands.measure.start('pageTimingMetrics30Days');
await commands.click.byLinkTextAndWait('Last 30 days');
await commands.measure.stop();
};
Will result in:
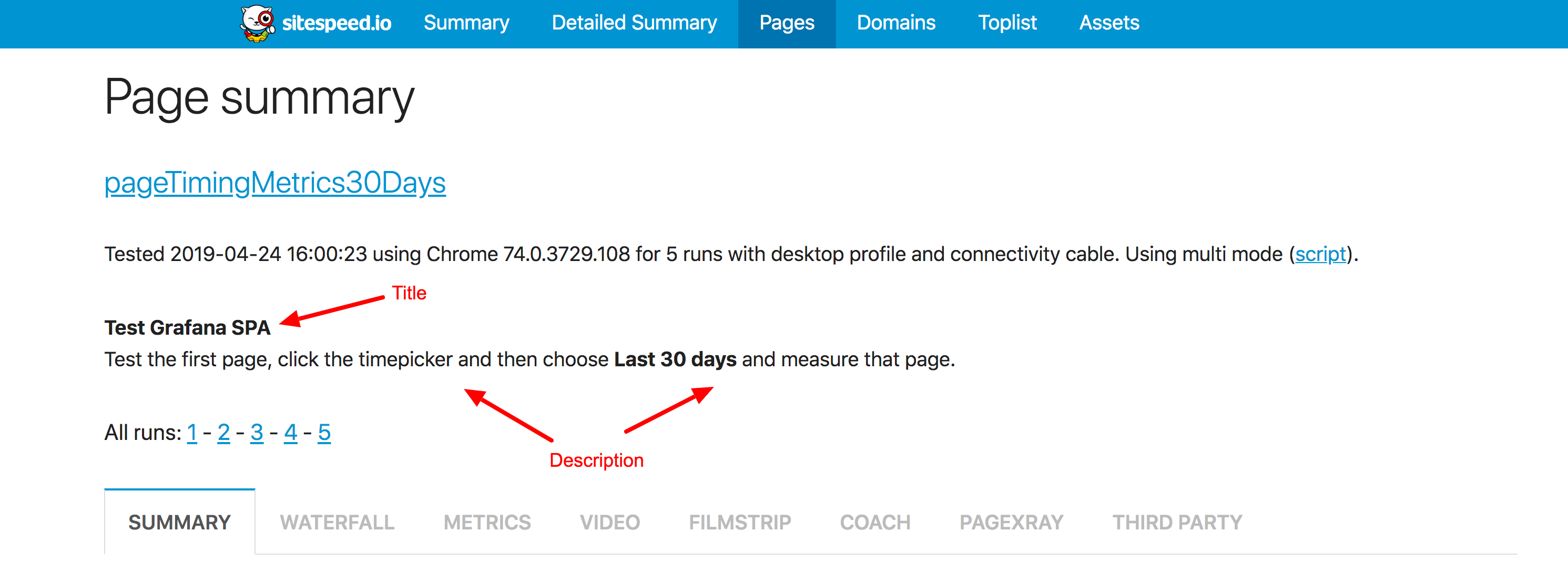
I like the meta data since it makes it much easier to remember what you are actually testing :)
Chrome DevTools Protocol #
You can now send messages to Chrome using the Chrome DevTools Protocol. You can send and send and get the result by using two different commands. This makes it possible for you implement almost whatever Chrome supports.
Here’s an example of injecting JavaScript that runs on every new document.
module.exports = async function(context, commands) {
await commands.cdp.send('Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument',{source: 'console.log("hello");'});
await commands.measure.start('https://www.sitespeed.io');
}
And if you need to get something back from Chrome, use the sendAndGet command.
module.exports = async function(context, commands) {
await commands.measure.start('https://www.sitespeed.io');
const domCounters = await commands.cdp.sendAndGet('Memory.getDOMCounters');
context.log.info('Memory.getDOMCounters %j', domCounters);
}
You can read all about scripting in the documentation.
/Peter