There are multiple ways to interact with the current page. We have tried to add the most common ways so you don't need to use Selenium directly, and if yoiu think something is missing, please create an issue.
Finding elements
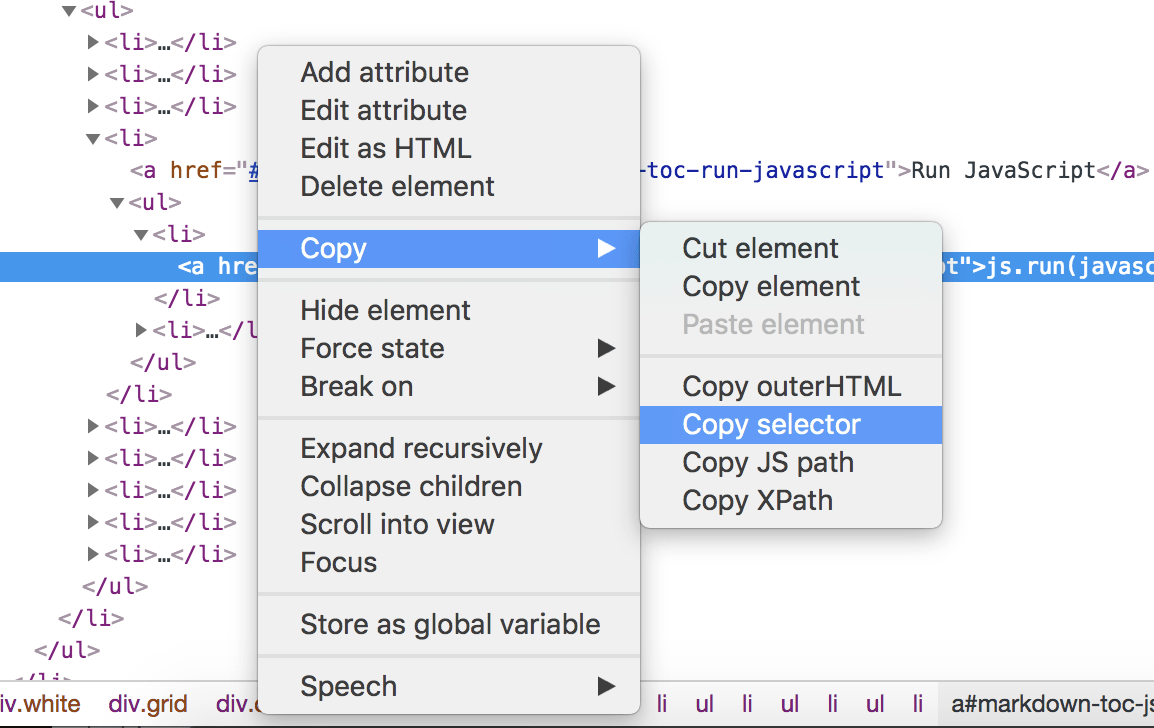
One of the key things in your script is to be able to find the right element to invoke. If the element has an id it’s easy. If not you can use developer tools in your favourite browser. The all work mostly the same: Open DevTools in the page you want to inspect, click on the element and right click on DevTools for that element. Then you will see something like this:
Using Safari to find the CSS Selector to the element
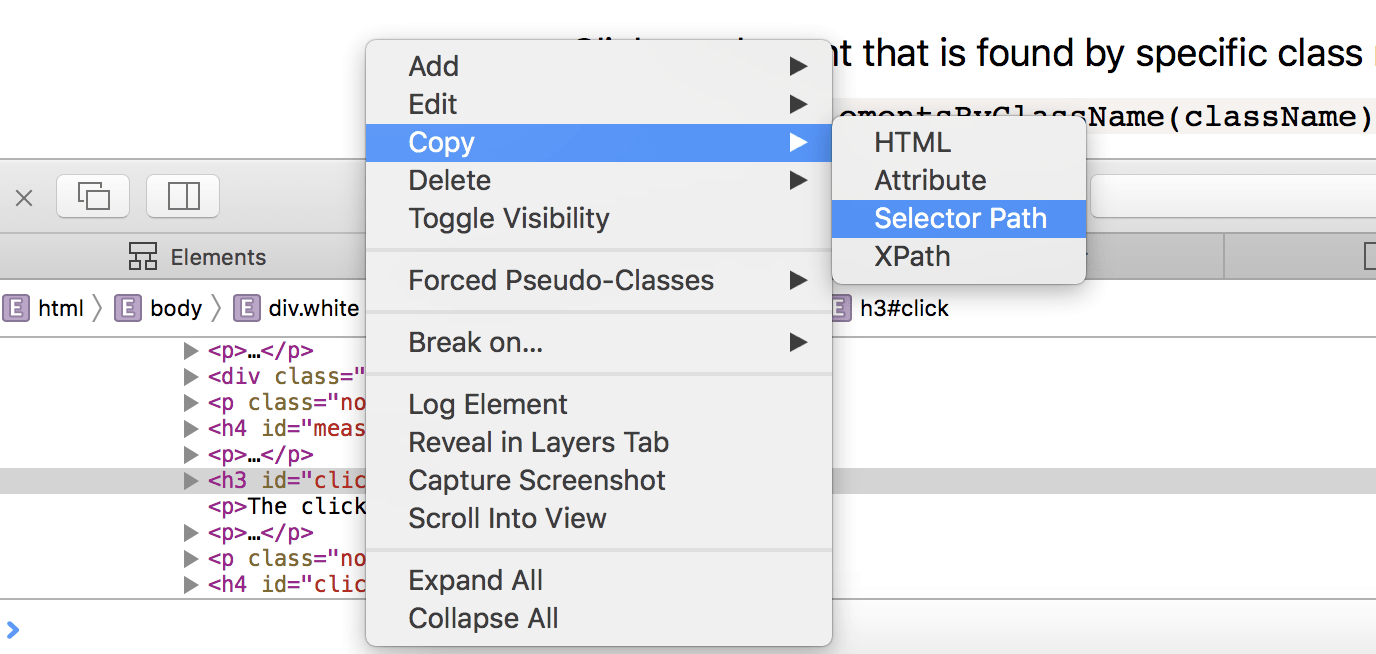
Using Firefox to find the CSS Selector to the element
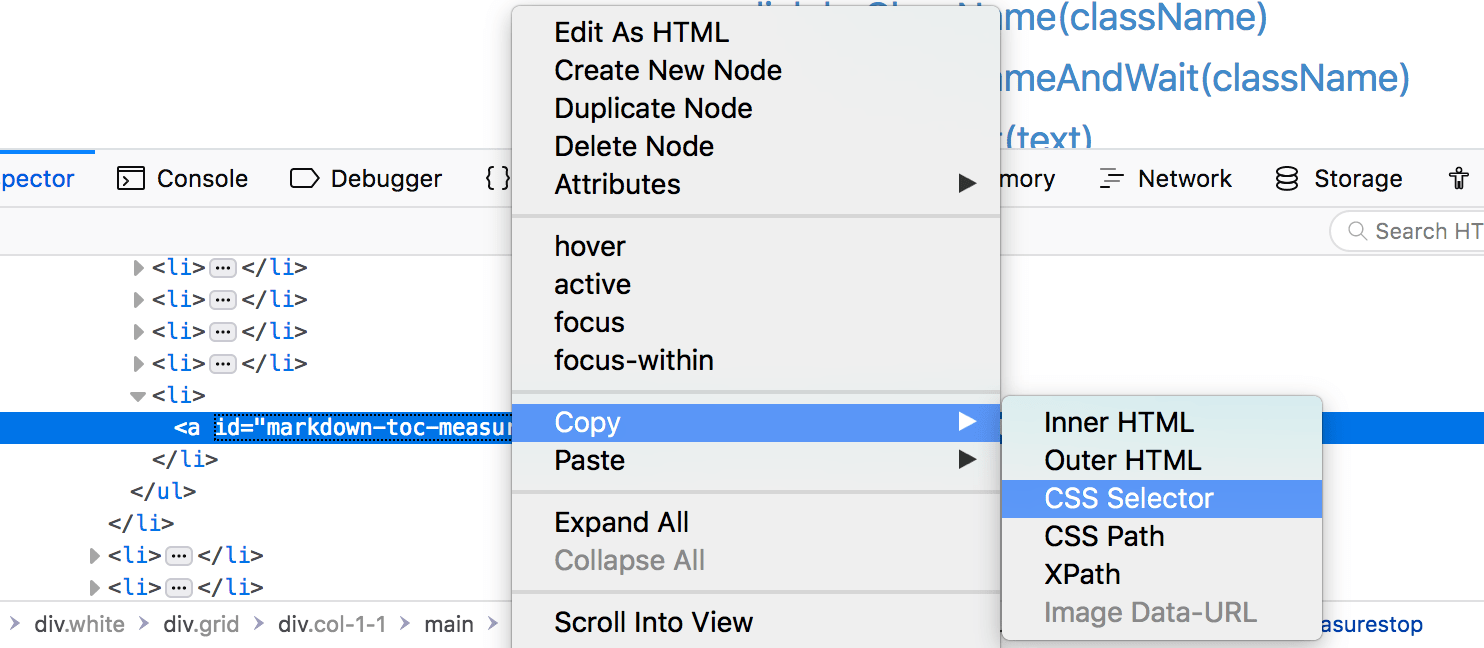 {
{
Using Chrome to find the CSS Selector to the element
Using Actions
Since Browsertime 21.0.0 we support easier access to the Selenium Action API. That makes easier to interact with the page and you can also chain commands. You can checkout the Selenium NodeJS Action API to see more what you can do.
Here's an example doing search on Wikipedia:
/**
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeContext} context
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeCommands} commands
*/
export default async function (context, commands) {
await commands.measure.start('https://www.wikipedia.org');
const searchBox = await commands.element.getById('searchInput');
const submitButton = await commands.element.getByClassName(
'pure-button pure-button-primary-progressive'
);
await commands.measure.start('Search');
await commands.action
.getActions()
.move({ origin: searchBox })
.pause(1000)
.press()
.sendKeys('Hepp')
.pause(200)
.click(submitButton)
.perform();
// If you would do more actions after calling .perform()
// you manually need to clear the action API
//await commands.action.clear();
await commands.wait.byPageToComplete();
return commands.measure.stop();
}
JavaScript
You can run your own JavaScript in the browser from your script. This is powerful because that makes it possible to do whatever you want :)
Run
Run JavaScript. Will throw an error if the JavaScript fails.
If you want to get values from the page, this is your best friend. Make sure to return the value and you can use it in your script.
/**
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeContext} context
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeCommands} commands
*/
export default async function (context, commands) {
// We are in browsertime context so you can skip that from your options object
const secretValue = await commands.js.run('return 12');
// if secretValue === 12 ...
}
By default this will return a Selenium WebElement.
Run and wait on page
Run JavaScript and wait for page complete check. Do that with commands.js.runAndWait("").
Click
The click command finds an element and runs .click() on the element.
Click commands have two different versions: One that will return a promise when the link has been clicked and one that will return a promise that will be fullfilled when the link has been clicked and the browser navigated to the new URL and the page complete check is done.
If it does not find the link, it will throw an error, so make sure to catch it if you want an alternative flow.
/**
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeContext} context
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeCommands} commands
*/
export default async function (context, commands) {
await commands.navigate('https://www.sitespeed.io/');
try {
await commands.click.byLinkText('Documentation');
await commands.click.byLinkTextAndWait('Documentation');
} catch(error) {
context.log.error('Could not find the link text "Documentation"', error);
}
}
All click commands
You can find all the click commands here.
Wait
There are a couple of wait commands that makes it easier to wait. Either you can wait on a specific id to appear, for x amount of milliseconds or for a page to finish loading.
Mouse
The mouse command will perform various mouse events using the Seleniums Action API.
Move
The mouse move commands.
Single click
Double click
Context click
Click and hold
Scroll
You can use scroll commands to scroll the browser window.
/**
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeContext} context
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeCommands} commands
*/
export default async function (context, commands) {
const delayTime = 250;
await commands.measure.start();
await commands.navigate(
'https://www.sitespeed.io/documentation/sitespeed.io/performance-dashboard/'
);
await commands.scroll.toBottom(delayTime);
return commands.measure.stop();
};
Add text
You can add text to input elements. The element needs to visible. You can also send pressable keys as Unicode PUA (PrivateUser Area) format.
The add text command.
Switch
You can switch to frames/windows or tabs using the the switch commands.
Set
Using the set commands you can set values to HTML elements.
Select
You can use the select command for selecting an option in a drop-down field.
Alert boxes
If you need to click on an alert box, the best way is to use Selenium directly. Here's an example on how to accept an alert box.
await context.selenium.driver.switchTo().alert().accept();