Run scripts using Browsertime is easy. Create your script and run it like this:
browsertime myScript.mjs
And in sitespeed.io you need to add the --multi switch (test multiple pages).
sitespeed.io myScript.mjs --multi
Multiple scripts
For multiple scripts, list them all in the command. This approach helps manage complex scripts by splitting them into multiple files.
sitespeed.io login.mjs measureStartPage.mjs logout.mjs --multi
Or you can break out code in multiple files.
Create a file to include exampleInclude.mjs
export async function example() {
console.log('This is my example function');
}
Then include it test.mjs:
import { example } from './exampleInclude.mjs';
export default async function (context, commands) {
example();
}
And then run it: sitespeed.io --multi test.mjs
Add meta data to your script
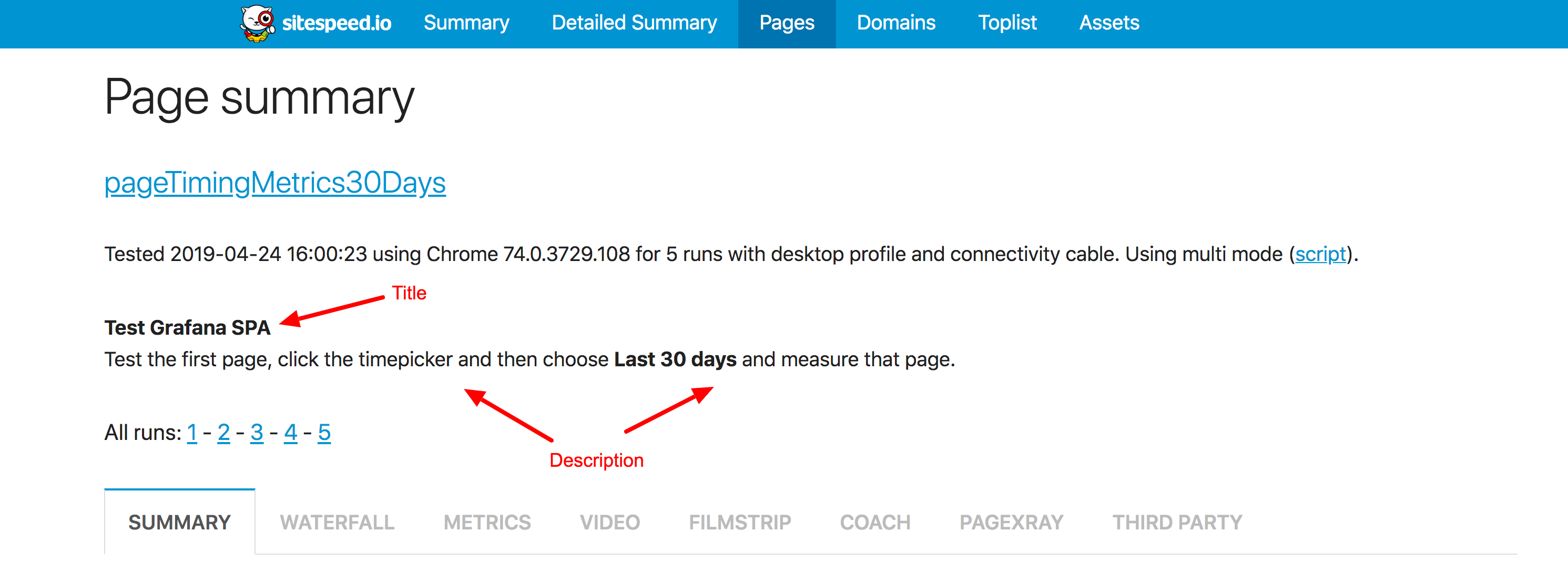
You can add meta data like title and description to your script. The extra data will be visible in the HTML result page.
Setting meta data like this:
/**
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeContext} context
* @param {import('browsertime').BrowsertimeCommands} commands
*/
export default async function (context, commands) {
commands.meta.setTitle('Test Grafana SPA');
commands.meta.setDescription('Test the first page, click the timepicker and then choose <b>Last 30 days</b> and measure that page.');
await commands.measure.start(
'https://dashboard.sitespeed.io/d/000000044/page-timing-metrics?orgId=1','pageTimingMetricsDefault'
);
await commands.click.byClassName('gf-timepicker-nav-btn');
await commands.wait.byTime(1000);
await commands.measure.start('pageTimingMetrics30Days');
await commands.click.byLinkTextAndWait('Last 30 days');
await commands.measure.stop();
};
Will result in: